Legal
Tenant Eviction Guide: Landlord Rights to Evict a Tenant Legally


Written by
Shivanshi Dheer
Read Time
9 min read
Posted on
July 14, 2025
Overview
Overview
Tenant Eviction Guide: Landlord’s Rights to Evict a Tenant Legally
As a PG or hostel owner, one of the most stressful situations you might face is dealing with a difficult or non-compliant tenant eviction. Whether it’s non-payment of rent, property damage, or violation of house rules, knowing when and how you can legally evict a tenant in India is essential to protect your rights.
This Tenant Eviction guide will walk you through everything you need to know about tenant eviction laws in India, from valid legal grounds to proper procedures, so that you can avoid unnecessary delays, disputes, or legal trouble.
What Does the Law Say About Tenant Eviction?
Eviction in India is a legal process designed to balance the rights of landlords with the protections afforded to tenants. Two primary laws govern tenancy and eviction:

Eviction of tenants in India is governed by:
Rent Control Acts (State-specific)
- Each Indian state enacts its own Rent Control Act or Rent Act (e.g., Maharashtra Rent Control Act, Tamil Nadu Buildings (Lease and Rent Control) Act).
- These Acts regulate rent levels, security deposits, lease durations, and eviction conditions within that state.
Transfer of Property Act, 1882
- Section 106–117 cover leases and define the contractual relationship between landlord and tenant.
- Provides general principles on lease creation, duration, and termination.
Key Principles:
- No Arbitrary Eviction: A tenant cannot be evicted without one of the valid grounds specified under the applicable Rent Control Act or the Transfer of Property Act.
- Due Process: Landlords must follow a formal court procedure serving notice, filing a suit, obtaining an eviction order before taking back possession.
- Tenant Rights: Tenants have the right to contest eviction grounds in court, present evidence, and request relief (e.g., stay orders, mediation).
- Landlord Rights: Landlords can reclaim property only for legal reasons such as non-payment of rent, breach of lease terms, personal requirement, or expiry of lease.
Understanding these laws helps PG and hostel owners avoid costly mistakes, build trust with tenants, and ensure any eviction is legally enforceable.
Grounds for Eviction of a Tenant in India
Here are the most common legal grounds for eviction:
| Ground | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Non-Payment of Rent | If a tenant fails to pay rent for a continuous period, landlords can initiate eviction. |
| Breach of Lease Agreement | Violating terms like unauthorized subletting, illegal use, or damage to property. |
| Owner’s Own Need | If the owner needs the property for self or family use. |
| Expiry of Lease / License Agreement | Refusal to vacate even after the lease ends. |
| Illegal Activities / Occupation | Use of the property for illegal purposes or overstaying without any contract. |
✅ Tip for PG/Hostel Owners: Always document any misconduct or non-payment, as it strengthens your case in court.
How to Evict a Tenant in India (Step-by-Step)
Evicting a tenant in India requires following a strict legal process to ensure fairness and avoid allegations of illegal eviction. Below is a detailed guide through each step, designed to help PG and hostel owners navigate the legal requirements:
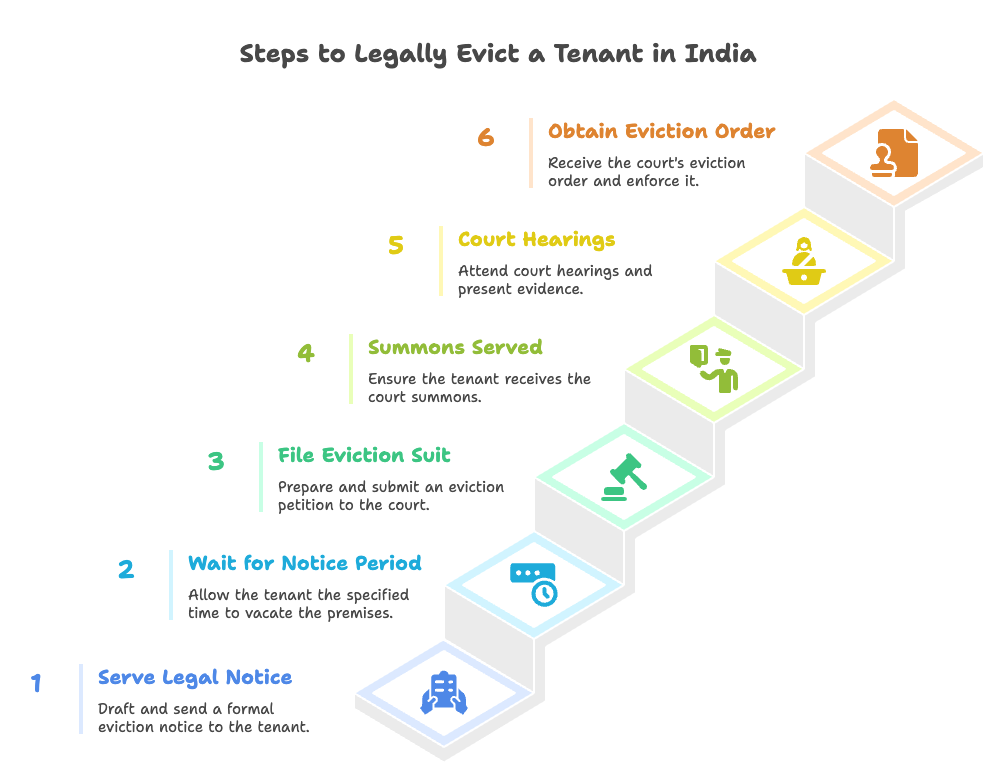
Step 1: Serve a Legal Notice
- Draft a written eviction notice clearly stating:
- Reason for eviction (e.g., non-payment of rent, lease breach, owner’s need).
- Reference to specific clauses in your rental agreement that have been violated.
- The timeframe to vacate the premises is usually 15 to 30 days, as allowed by state law or the agreement.
- Send the notice via registered post with acknowledgment due, or deliver it through your legal counsel to provide proof of service.
This ensures the tenant is formally informed and creates a paper trail critical for court proceedings.
Step 2: Wait for the Notice Period
- Allow the tenant the full notice period to vacate.
- Keep written records of any tenant response or lack thereof.
Courts will require proof that you gave the tenant a fair chance to comply.
Step 3: File an Eviction Suit
- If the tenant does not vacate by the notice deadline, prepare an eviction petition under the applicable state’s Rent Control Act.
- Attach supporting documents:
- Copy of the rent agreement.
- Proof of notice service (acknowledgment receipts).
- Rent payment records and any breach documentation.
- Submit the petition in the civil court having jurisdiction over your property.
This initiates the formal legal process, and courts base their judgment on the completeness of your documentation.
Step 4: Summons Is Served
- The court clerk issues a summon to the tenant, requiring their appearance.
- Ensure the tenant receives the summon either in person or via registered mail.
The tenant must also be given the opportunity to present their defense.
Step 5: Court Hearings
- Preliminary hearing to confirm the validity of your petition.
- Evidence presentation by both parties:
- You present the rental agreement, notice proof, payment defaults, and breach records.
- The tenant may present counter-evidence or defenses.
- The court may attempt mediation before a full trial.
Strong, organized evidence can expedite the judgment, and mediation can resolve disputes faster with mutual agreement.
Step 6: Obtain the Court’s Eviction Order
- If the court rules in your favor, you receive an eviction order.
- Provide the tenant with a copy of the decree and a final vacate deadline.
- If the tenant still refuses, file an execution petition with the court to enlist the help of local police or civil authorities.
Only a court order legitimizes eviction, and enforcement by authorities prevents accusations of self-help eviction.
How to Avoid Illegal Eviction in India
Eviction without following proper legal procedures can land landlords in serious legal trouble and damage their reputation. Here are some common illegal eviction tactics to avoid, and the correct approach to handle each situation:
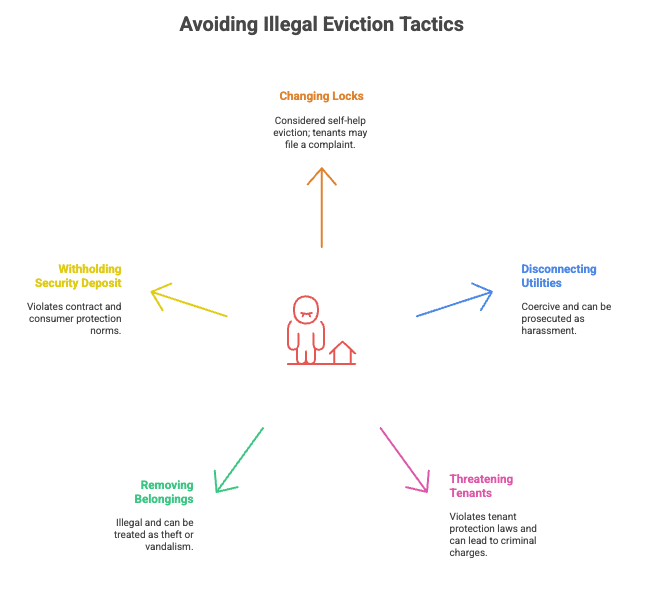
| Illegal Action | Why It’s Wrong | Legal Alternative |
| Changing Locks | Considered self-help eviction; tenants may file a complaint for unlawful dispossession and recover damages. | Follow the court-ordered eviction process to obtain a valid distress warrant or eviction order before taking possession. |
| Disconnecting Utilities | Cutting off water, electricity, or gas is coercive and can be prosecuted as harassment. | Issue a legal notice for non-payment of utility charges (if specified in agreement) or seek a court directive for dues recovery. |
| Threatening or Forcing Tenant Out | Intimidation, threats, or physical force violate tenant protection laws and can lead to criminal charges against the landlord. | Serve a formal eviction notice and file an eviction suit if the tenant fails to comply with the notice period. |
| Removing Belongings | Disposing or removing tenant’s possessions is illegal and can be treated as theft or vandalism. | Use court-approved procedures and, if necessary, a bailiff or local police presence to oversee property handover post-eviction. |
| Withholding Security Deposit | Unreasonably retaining the entire deposit without proper accounting or notice violates contract and consumer protection norms. | Deduct only documented damages or unpaid dues, provide an itemized statement, and return the balance within the timeframe mandated by law. |
⚖️ Consequences of Illegal Eviction
- Legal Penalties: Fines, compensation to the tenant, and possible criminal charges for harassment or wrongful eviction.
- Court Orders in Tenant’s Favor: Courts may order tenant restoration, damages, and legal costs, reversing any informal eviction.
- Reputation Damage: Negative word-of-mouth and reduced trust from future tenants.
✅ Best Practices to Stay Compliant
- Always Serve Notice & Obtain Court Order: Never resort to self-help measures.
- Document Communication: Keep copies of all notices, receipts, emails, and messages.
- Seek Legal Advice: Consult a qualified lawyer before initiating eviction, especially in complex cases.
- Maintain Professionalism: Treat tenants respectfully—even during disputes—to minimize conflict and possible escalation.
By following these guidelines and adhering strictly to legal procedures, PG and hostel owners can protect their property rights while maintaining ethical standards and avoiding costly litigation.
What to Do If a Tenant Doesn’t Pay Rent
Consistent rent payment is the lifeblood of your rental business. When a tenant misses payments, follow these steps to encourage compliance and protect your legal standing:
1. Send Written Payment Reminders
- Draft polite reminders via email, WhatsApp, or letter.
- Mention the overdue amount, original due date, and any late fees as per your agreement.
Establishes proof that you notified the tenant of missed dues. Often prompts timely payment without escalating to legal action.
>> Use RentOk for this, it is legally compliant and will automatically send the dues messages and track how much is due.
2. Refer to Rental Agreement Clauses
- Highlight the specific clause in your agreement regarding payment terms and penalties.
- Remind the tenant of the consequences for continued non-payment (e.g., late fees, eviction notice).
Reinforces that the tenant agreed to these terms voluntarily. This will strengthen your position if you need to pursue legal remedies.
3. Issue a Formal Eviction Notice
- If payment isn’t made within the grace period (usually 7–15 days after a reminder), serve a formal eviction notice.
- Use registered post or legal counsel to ensure proof of delivery.
Marks the transition from reminder to legal action. It creates an official record required for court proceedings.
4. Keep Detailed Records
- Archive all reminders, notices, payment receipts, and tenant responses.
- Use digital tools (like RentOk) to log every interaction with timestamps.
Complete documentation is your strongest asset in court. It demonstrates your fair and systematic approach.
5. File an Eviction Suit with Evidence
- If the tenant still fails to pay or vacate, prepare an eviction petition with all collected evidence.
- File it in the appropriate civil court under the local Rent Control Act.
Initiates the formal eviction process. Courts rely heavily on documented proof of your attempts to resolve the issue amicably.
Pro Tip: Use a rent management system to automate reminders, track payment history, and store documentation in one place making dispute resolution faster and smoother.
Things Landlords Should Know Before Evicting a Tenant
| Checklist Item | Why It’s Important |
| Understand local eviction laws | Rent laws vary by state. Know your state’s rules. |
| Have a valid reason | Courts won’t allow arbitrary eviction. |
| Document everything | Agreements, payment records, and notices are key. |
| Respect tenant rights | Following due process strengthens your case in court. |
Final Thoughts: Eviction Doesn’t Have to Be a Battle
Evicting a tenant can be stressful, but if you follow legal steps and respect tenant rights, the process is manageable and justified. For PG and hostel owners, especially, legal compliance builds credibility and protects your income.
Try RentOk: The Smarter Way to Manage Tenants
RentOk is designed to help landlords and PG owners:
- Track rent payments
- Automate reminders
- Create & manage rental agreements
- Keep a digital record of notices and dues
Our Eviction Notice feature & legal services can help you in managing all these things!
FAQs on Tenant Eviction in India
Q1. What is the Indian Rent Control Act?
It governs tenant-landlord relationships in various states, protecting tenants from arbitrary rent hikes and evictions.
Q2. Who is eligible for eviction under this act?
Tenants who violate agreement terms, don’t pay rent, damage property, or overstay the post-agreement expiry.
Q3. What is an eviction notice?
A formal letter/legal document informing the tenant to vacate the property within a given period.
Q4. How is an eviction notice served?
Usually by registered post, courier, or legal email/WhatsApp with delivery confirmation.
Q5. What is the time frame for eviction after a notice is served?
Typically, 15–30 days, depending on the agreement or the court’s discretion.
Q6. What is the role of the court?
The civil court hears both parties and grants eviction if the landlord’s case is valid.

About the Author
Shivanshi Dheer
Shivanshi Dheer sharing actionable strategies and information on PG/hostel management to help simplify renting and scale with RentOk.










